

The last four consonant sounds on the above list – “y”, “w”, “r”, “l” – are produced with less mouth constriction than other consonants, and in linguistics are called “approximants”.Īpproximants occupy a kind of linguistic grey area between vowels and consonants, in fact “w” and “y” are also known as semivowels.

(Just ignore the “c” with a cedilla, it’s slicing things a bit fine IMHO. One of my new favourite things is the free version of the Cued Articulation iPad app, which contains this handy consonant chart, which you might like to refer to in what follows: And to complicate matters, many English vowels are technically two or three vowels shmooshed together. Most syllables contain a vowel, though vowel-like consonants can occasionally be syllables. Only a few children with severe speech sound difficulties (often called dyspraxia or apraxia) sometimes need therapy to help them produce vowel sounds correctly.
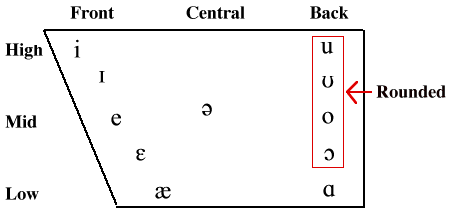
When we talk, consonants break up the stream of vowels (functioning as syllable onsets and codas), so that we don’t sound like we’ve just been to the dentist for four fillings and the anaesthetic hasn’t worn off yet.Ĭonsonants require more precise articulation than vowels, which is why children find them harder to learn, and often end up in speech therapy after having become so cross at not being understood that they’ve started hitting people. The difference between vowels and consonantsĪ vowel is a speech sound made with your mouth fairly open, the nucleus of a spoken syllable.Ī consonant is a sound made with your mouth fairly closed. Depending on your accent and how thinly you slice them, there are about 20 vowels and 24 consonants. Vowels and consonants are sounds, not letters. There are five vowels and 21 consonants in English, right? Well, no. The difference between consonants and vowels 48 Replies


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
